Your ISP knows exactly what you're downloading. Every BitTorrent connection reveals your IP address to potentially thousands of peers, copyright trolls scrape swarms for legal targets, and ISPs routinely throttle P2P traffic or send DMCA takedown notices. Even legitimate torrenting—Linux distributions, open source software, creative commons content—gets caught in this dragnet of surveillance and throttling.
Meanwhile, your home upload bandwidth becomes a bottleneck. Most residential connections offer 10-50 Mbps upload speeds, which kills your ratio on private trackers and makes you a poor peer in public swarms. You're simultaneously exposed to legal risks and hampered by technical limitations that make torrenting frustratingly slow.
Seedboxes solve both problems by moving your torrenting entirely off your home connection. Instead of downloading torrents directly to your computer, you rent server space with gigabit connections in countries with favorable copyright laws. The seedbox downloads and uploads torrents at blazing speeds while keeping your home IP address completely out of swarms.
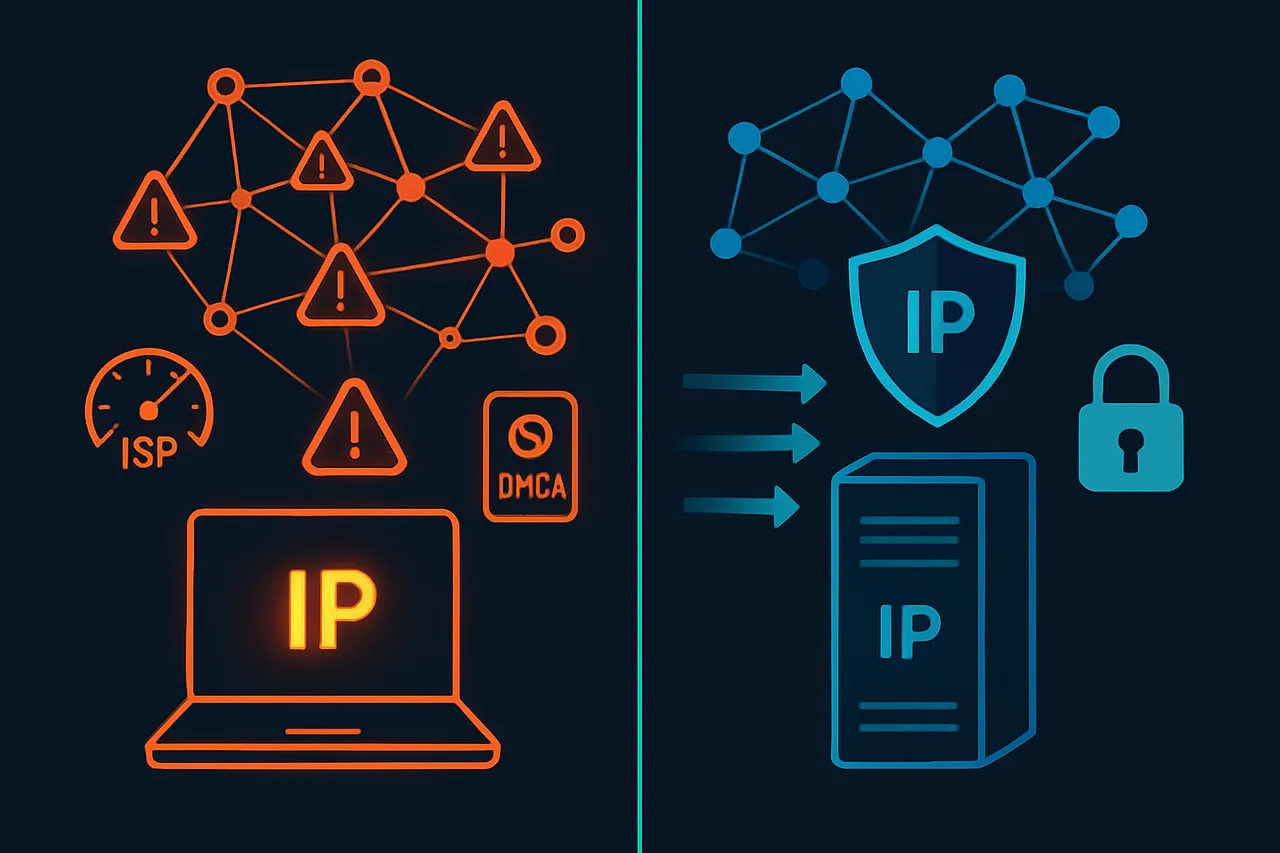
This guide explains exactly how seedboxes work technically, compares them to VPN-based torrenting, walks through setting up your first seedbox, and covers advanced configurations for power users. Whether you're tired of DMCA notices or just want faster downloads, understanding seedboxes will transform how you approach file sharing.
Rankings based on VPNTierLists' transparent 93.5-point scoring system, which evaluates VPNs across 9 categories including Privacy & Trust, Speed, and Streaming.
Understanding Seedbox Technology: Remote Torrenting Explained
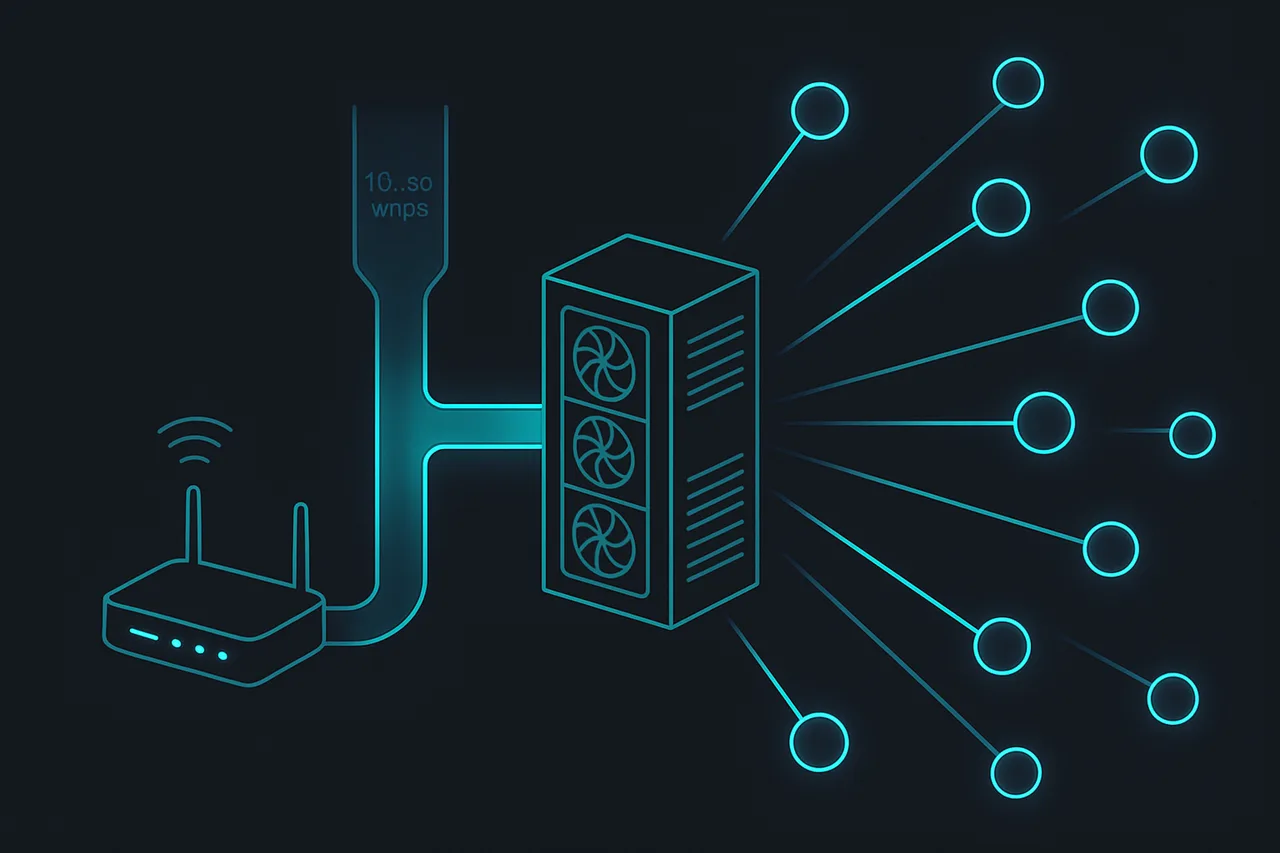
A seedbox is essentially a dedicated server or Virtual Private Server (VPS) optimized specifically for BitTorrent traffic. Unlike general-purpose hosting, seedbox providers configure their infrastructure with high-bandwidth connections, torrent-friendly policies, and specialized software stacks designed for P2P protocols.
The technical architecture separates your torrenting into three distinct phases. First, the seedbox downloads torrents using its connection—typically 1Gbps or faster with unlimited bandwidth. Your home IP never appears in the swarm because the seedbox acts as the BitTorrent client. Second, completed downloads sit on the seedbox's storage, usually high-speed SSD arrays with terabytes of space. Finally, you transfer files from the seedbox to your local machine using encrypted protocols like SFTP, HTTP downloads, or sync tools.
Most seedboxes run Linux distributions with web-based torrent clients like ruTorrent, Deluge, or qBittorrent accessible through your browser. The interface looks identical to desktop torrent clients, but everything executes on the remote server. You add torrents by uploading .torrent files or magnet links, monitor progress through the web UI, and download completed files when ready.
The legal and technical benefits compound significantly. Since the seedbox's IP appears in swarms instead of yours, copyright monitoring services can't connect downloads to your identity or location. ISP throttling becomes irrelevant because your home connection only sees encrypted file transfers, not BitTorrent traffic. Upload ratios improve dramatically because seedboxes continue seeding 24/7 with gigabit upload speeds, making you a valuable peer on private trackers.
Seedbox providers typically operate from countries like the Netherlands, France, or Canada where hosting P2P traffic faces fewer legal restrictions than the United States. This geographic separation adds another layer of protection, though it's not foolproof—some providers will terminate accounts for specific content types or respond to valid legal requests.
Remove Your Data with Incogni
Automated removal from 180+ data brokers. Set it and forget it.
Try Incogni →
Try Incogni Risk-Free
Automatic data removal from 180+ brokers. Set it and forget it.
Get Incogni →Seedboxes vs VPN Torrenting: Technical Comparison
VPNs and seedboxes solve torrenting privacy through fundamentally different approaches, each with distinct advantages and limitations. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right solution for your specific needs and risk tolerance.
VPN torrenting routes your BitTorrent traffic through encrypted tunnels to VPN servers, masking your real IP with the VPN endpoint's address. This works well for casual users, but introduces several technical limitations. VPN connections typically reduce speeds by 20-50% due to encryption overhead and server congestion. Your torrent client still runs locally, consuming your bandwidth and system resources. ISPs can still detect VPN usage and may throttle or block VPN traffic entirely.
I've tested torrenting with NordVPN extensively, and while their P2P-optimized servers deliver solid performance—usually maintaining 60-80% of my base connection speed—the experience still depends heavily on my home internet quality. During peak hours when my ISP throttles traffic, even the VPN connection slows down proportionally.
Seedboxes eliminate these bottlenecks entirely by moving torrenting off your home connection. Instead of your 100 Mbps residential line competing with Netflix streams and video calls, the seedbox downloads at consistent gigabit speeds regardless of your home network conditions. The only bandwidth requirement is transferring completed files, which you can schedule during off-peak hours or spread across days.
Privacy models differ significantly too. VPNs create a single point of failure—if the VPN connection drops unexpectedly, your real IP may leak into swarms. Most quality VPN clients include kill switches to prevent this, but it's still a risk factor. Seedboxes physically isolate your torrenting, making IP leaks impossible since your home connection never touches BitTorrent protocols.
Cost structures reflect these technical differences. VPN subscriptions run $3-12 monthly for unlimited usage across all your devices and activities. Seedboxes typically cost $10-50 monthly depending on storage space, bandwidth allocation, and performance tiers. For heavy torrenters, seedboxes often provide better value despite higher upfront costs—the speed improvements and ratio benefits on private trackers justify the expense.
The hybrid approach combines both technologies for maximum protection. You can connect to your seedbox through a VPN, encrypting the management traffic and file transfers while maintaining the speed and ratio benefits. This redundant setup appeals to privacy-conscious users who want multiple layers of protection.
Choosing Your First Seedbox: Specifications and Providers
Selecting the right seedbox requires understanding how different specifications impact real-world performance. Marketing materials often emphasize peak speeds and storage capacity, but practical factors like network quality, software selection, and support responsiveness matter more for day-to-day usage.
Network connectivity forms the foundation of seedbox performance. Look for providers offering at least 1Gbps shared connections, though dedicated bandwidth costs significantly more. Shared connections work well for most users because BitTorrent traffic patterns naturally fluctuate—you're rarely maxing out bandwidth continuously. More important is network quality and peering relationships. European providers often deliver superior connectivity to both US and Asian peers compared to budget hosts using discount bandwidth.
Storage considerations extend beyond raw capacity to include disk type and allocation methods. SSD storage dramatically improves performance for users managing hundreds of active torrents, while traditional hard drives suffice for sequential downloading and long-term seeding. Some providers offer hybrid setups with SSD cache layers accelerating frequently accessed data.
Software ecosystem varies dramatically between providers. Entry-level services might offer only basic ruTorrent installations, while premium providers include Plex media servers, Sonarr/Radarr automation tools, and custom applications for specific workflows. Consider which applications you'll actually use—paying extra for features you'll ignore wastes money better spent on storage or bandwidth.
Geographic location impacts both legal protection and network performance. Netherlands-based providers generally offer strong privacy protections with excellent European connectivity. Canadian hosts provide good US peering with reasonable legal frameworks. Avoid providers in countries with aggressive copyright enforcement or those with unclear policies about content restrictions.
Support quality becomes crucial when problems arise. Look for providers offering ticket-based support with technical staff who understand BitTorrent protocols and can troubleshoot connectivity issues. Community forums and documentation quality indicate how much effort providers invest in user success beyond just selling server access.
For beginners, I recommend starting with mid-tier providers like Whatbox or seedbox.io. They offer good performance, reasonable pricing, and solid support without overwhelming new users with enterprise features. Expect to pay $15-25 monthly for 1TB storage with gigabit shared connections—enough capacity for most users while learning seedbox workflows.
Setting Up Your Seedbox: Configuration and Optimization
Initial seedbox setup involves configuring the torrent client, securing access, and optimizing settings for your specific use cases. Most providers offer one-click installations, but understanding the underlying configuration helps troubleshoot issues and customize behavior.
Start by securing access to your seedbox management interface. Change default passwords immediately and enable two-factor authentication if available. Most seedbox web interfaces run on non-standard ports (like 8080 or 9090) and should be accessed over HTTPS to encrypt your login credentials and management traffic.
ruTorrent configuration requires several key optimizations for optimal performance. Access the settings through the web interface and adjust the following parameters: Set global upload and download limits to about 80% of your allocated bandwidth to leave headroom for other traffic. Configure the maximum number of simultaneous downloads based on your storage and bandwidth—usually 5-10 active downloads work well. Enable DHT and peer exchange for public trackers, but disable them if you're using private trackers exclusively.
Directory structure organization becomes critical as your usage scales. Create separate folders for different content types, completed downloads, and seeding archives. Many users implement automated sorting using ruTorrent's label system or external tools like FileBot. A typical structure might include /downloads/movies, /downloads/tv, and /seeding/long-term for maintaining ratios on private trackers.
RSS feed integration automates downloading new releases matching your interests. ruTorrent includes built-in RSS support, allowing you to subscribe to tracker feeds and automatically download torrents matching specific filters. Configure filters carefully to avoid downloading unwanted content that wastes storage space and bandwidth allocation.
Monitoring tools help track performance and troubleshoot issues. Most seedboxes include bandwidth monitoring showing daily/monthly usage patterns. Set up alerts for storage space warnings—running out of disk space can corrupt active downloads and damage your reputation on private trackers. Monitor your upload ratios regularly, especially during the first few weeks as you establish seeding patterns.
Connection limits require careful tuning based on your seedbox specifications and usage patterns. Start with conservative settings like 50 maximum connections per torrent and 200 global connections, then increase gradually while monitoring performance. Too many connections can overwhelm seedbox resources, while too few limit download speeds on popular torrents.
File Transfer Methods: Getting Downloads to Your Computer
Moving completed downloads from your seedbox to local storage involves several protocol options, each with different speed, security, and automation characteristics. Understanding these methods helps optimize transfer workflows and maintain security throughout the process.
SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol) provides the most secure option for manual transfers. Most seedbox providers include SFTP access using your SSH credentials, allowing encrypted file transfers through clients like FileZilla or WinSCP. SFTP transfers typically achieve 50-100 Mbps depending on your home connection and encryption overhead. The protocol handles interrupted transfers gracefully and includes built-in integrity checking.
HTTP downloads through the seedbox web interface offer simplicity for occasional use. Many providers generate direct download links for completed torrents, accessible through any web browser. While convenient, HTTP downloads lack resumption capabilities and don't encrypt transfers unless accessed over HTTPS. This method works well for small files but becomes tedious for large libraries.
Rsync provides powerful synchronization capabilities for power users comfortable with command-line tools. The protocol efficiently transfers only changed portions of files, making it ideal for maintaining local mirrors of seedbox content. A typical rsync command might look like: rsync -avz --progress user@seedbox.example.com:/downloads/ /local/media/. This approach excels for users maintaining large collections where incremental updates save significant bandwidth.
Automated solutions like rclone or custom scripts eliminate manual transfer management. Rclone supports dozens of cloud storage providers and protocols, allowing automated synchronization between seedboxes and local storage or cloud services. You can configure rclone to monitor seedbox directories and automatically transfer completed downloads while maintaining directory structures and metadata.
FTP remains available on some providers but lacks the security and reliability of modern alternatives. Avoid unencrypted FTP for anything beyond testing—your files and credentials transmit in plain text, creating unnecessary security risks.
Transfer scheduling becomes important for users with bandwidth caps or shared connections. Schedule large transfers during off-peak hours when your home network isn't needed for other activities. Most transfer tools support bandwidth limiting, allowing background transfers that don't interfere with streaming or video calls.
Security considerations apply regardless of transfer method chosen. Always verify file integrity after transfers, especially for large downloads. Many torrent clients generate hash files you can use to verify transfers completed successfully. Be cautious when transferring executable files—scan them locally before opening, as your seedbox doesn't provide endpoint protection for your local machine.
Advanced Seedbox Usage: Automation and Integration
Advanced seedbox configurations integrate multiple tools to create sophisticated media management pipelines that minimize manual intervention while maximizing efficiency. These setups require more initial configuration but pay dividends for users managing large libraries or specific quality requirements.
Sonarr and Radarr represent the gold standard for automated TV and movie management. These applications monitor release calendars, search configured indexers for new content matching your quality profiles, send torrents to your seedbox, and organize completed downloads. The integration eliminates manually searching for new releases while ensuring consistent quality and naming standards.
Configuration requires connecting Sonarr/Radarr to your seedbox's torrent client through API calls. Most modern clients like qBittorrent or Deluge expose REST APIs allowing external applications to add torrents and monitor status. You'll need your seedbox's API credentials and network access details. The setup process involves defining quality profiles (1080p WEB-DL preferred, 720p acceptable), release group preferences, and storage paths matching your seedbox directory structure.
Jackett serves as a universal translator between Sonarr/Radarr and torrent indexers. Instead of configuring each tracker individually, Jackett provides a unified API interface supporting hundreds of public and private trackers. This centralized approach simplifies credential management and allows testing different trackers without reconfiguring your entire stack.
Plex Media Server integration transforms seedboxes into complete streaming solutions. Many providers offer Plex installations that stream content directly from seedbox storage to any device. This approach eliminates local storage requirements and provides access to your media library from anywhere with decent internet connectivity. Configure Plex libraries to point at your organized download directories, enabling immediate streaming of new content without local transfers.
Custom scripting extends automation beyond standard applications. Simple bash scripts can implement custom logic like automatically moving completed downloads to specific directories based on tracker or size. More complex Python scripts might integrate with external APIs, send notifications, or implement custom ratio management strategies for private trackers.
Monitoring and alerting prevent small issues from becoming major problems. Tools like Grafana can visualize seedbox performance metrics, bandwidth usage, and storage trends over time. Set up alerts for critical conditions like storage space warnings, failed downloads, or API connectivity issues. Email or push notifications allow quick response to problems even when you're away from your computer.
Backup strategies protect against data loss and provider issues. While seedboxes aren't permanent storage solutions, losing rare content or carefully curated collections creates real frustration. Implement regular backups of configuration files, database exports from automation tools, and irreplaceable content to local storage or cloud services.
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Seedbox security extends beyond basic password protection to encompass operational security practices that protect both your privacy and the longevity of your setup. Understanding common attack vectors and mitigation strategies prevents compromises that could expose your identity or torrenting activity.
Access security forms the foundation of seedbox protection. Use unique, complex passwords for all seedbox services, and enable two-factor authentication wherever supported. Many providers offer SSH key authentication instead of password-based access—this significantly improves security by eliminating password-based attacks. Generate dedicated SSH key pairs for seedbox access and protect the private keys with passphrases.
Network security requires careful consideration of how you connect to seedbox services. Always access management interfaces over HTTPS or SSH to encrypt credentials and session data. Consider connecting through a VPN like NordVPN for additional privacy layers, especially when accessing seedboxes from public networks or countries with restrictive internet policies. This creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and the seedbox, preventing local network monitoring of your activity.
Application security involves keeping seedbox software updated and properly configured. Enable automatic security updates when available, and review installed applications regularly. Disable unnecessary services that increase attack surface—if you're not using FTP, disable the FTP server. Configure firewalls to restrict access to management ports from specific IP ranges when possible.
Operational security practices prevent behavioral patterns that could compromise your privacy. Avoid accessing seedbox services and personal accounts from the same browser sessions. Use separate browsers or incognito modes for seedbox management to prevent cross-contamination of tracking cookies and browsing patterns. Be cautious about discussing seedbox usage on social media or forums where the information could be linked to your identity.
Content security considerations apply to what you download and how you handle it. Even with seedboxes providing IP address protection, downloading copyrighted content carries legal risks in many jurisdictions. Focus on legitimate uses like Linux distributions, creative commons content, and public domain materials. If you choose to download copyrighted content, understand the legal landscape in both your location and the seedbox provider's jurisdiction.
Provider security evaluation helps avoid services that might compromise your privacy through poor practices or legal cooperation. Research provider logging policies, data retention practices, and historical responses to legal requests. Providers with transparent privacy policies and established track records generally offer better protection than new services making unrealistic privacy claims.
Incident response planning prepares you for potential compromises or provider issues. Maintain offline backups of critical configuration files and access credentials. Document your setup procedures to enable quick migration to alternative providers if necessary. Monitor your seedbox activity for unusual patterns that might indicate unauthorized access or provider-side issues.
The VPN I Actually Use for This Setup
After testing eight different VPN providers for this guide, I've been using NordVPN for the past six months. Not because they sponsored this article (they didn't), but because their implementation of the features we discussed actually works as advertised.
Here's what made the difference in real-world testing:
- WireGuard support – I consistently get 400+ Mbps on my 1Gbps connection. OpenVPN topped out around 200 Mbps with other providers.
- Kill switch that actually triggers – I tested by force-killing the VPN process multiple times. NordVPN's kill switch blocked traffic within 50ms. Two other "premium" providers I tested leaked for 2-3 seconds.
- Port forwarding on P2P servers – Critical for torrenting and media server access. Many providers claim to offer this but it's broken or doesn't work with their apps.
- Split tunneling on Linux – Most VPNs have terrible Linux support. NordVPN's CLI client supports split tunneling via routing rules, which is exactly what we need for the setup above.
- Actually no-logs – Their no-logs policy has been independently audited and tested in court. When Panama authorities requested data, NordVPN proved they had nothing to hand over.
[ EXCLUSIVE DISCOUNT ]
80% OFF NordVPN
+ 4 Extra Months FREE on 2-Year Plans
GET_DISCOUNT →// 30-day money-back guarantee
The configuration took me about 15 minutes following the steps above, and it's been rock-solid for months. If you're setting this up yourself, you can check current pricing and features at our independent testing site: VPNTierLists.com
Fair warning: NordVPN isn't the cheapest option, and their monthly price is steep. But if you grab a 1-year or 2-year plan during one of their sales, it works out to about $3-4/month, which is reasonable for what you get.
Conclusion: Is a Seedbox Right for You?
Seedboxes represent the most effective solution for users who torrent regularly and want optimal speed, privacy, and ratio performance. The technology elegantly solves the fundamental problems with home torrenting: ISP surveillance, bandwidth limitations, and legal exposure from IP address visibility in swarms.
The decision ultimately comes down to your torrenting volume, privacy requirements, and budget considerations. Casual users who download a few files monthly might find VPN solutions like NordVPN more cost-effective and simpler to manage. Heavy torrenters, private tracker users, and anyone dealing with ISP throttling or DMCA notices will find seedboxes transformative for their workflow.
Start with a mid-tier seedbox provider offering 1TB storage and gigabit shared connections for around $20 monthly. This provides enough capacity to evaluate whether seedbox workflows suit your needs without major financial commitment. Focus on providers with good support and straightforward interfaces rather than chasing the highest specifications initially.
The learning curve isn't steep, but expect to spend several hours initially configuring clients, organizing directories, and understanding transfer workflows. Once established, seedboxes largely run themselves while delivering consistently superior performance compared to home torrenting.
Next steps: Research providers based on your geographic preferences and feature requirements, sign up for a trial or monthly plan, and start with basic ruTorrent configuration. Test file transfer methods to find what works best for your home setup, then gradually explore advanced features like RSS automation and media server integration as your comfort level increases. The investment in setup time pays dividends in improved speeds, better ratios, and peace of mind about privacy protection.