TL;DR: Configure split tunneling to route only torrent traffic through your VPN while keeping other applications on your regular connection. This comprehensive guide covers qBittorrent configuration, VPN kill switches, port forwarding, IP leak testing, and legal considerations across multiple operating systems.
Rankings based on VPNTierLists' transparent 93.5-point scoring system, which evaluates VPNs across 9 categories including Privacy & Trust, Speed, and Streaming.
Why This Matters: The Critical Need for Secure Torrent Routing
Torrenting without proper protection is like leaving your front door wide open with a sign that says "come on in." Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can see every torrent you download, copyright holders can track your IP address, and you're exposed to potential legal action or throttling. However, routing all your internet traffic through a VPN creates its own problems: slower speeds for regular browsing, potential streaming service blocks, and unnecessary encryption overhead for activities that don't require anonymity.
Split tunneling solves this dilemma by creating a selective routing system where only your torrent client connects through the VPN tunnel, while your web browser, streaming services, and other applications use your regular internet connection. This approach gives you the best of both worlds: complete anonymity for torrenting activities and full-speed access for everything else. The stakes here are significant – copyright infringement notices, ISP throttling, and potential legal consequences can all be avoided with proper configuration.
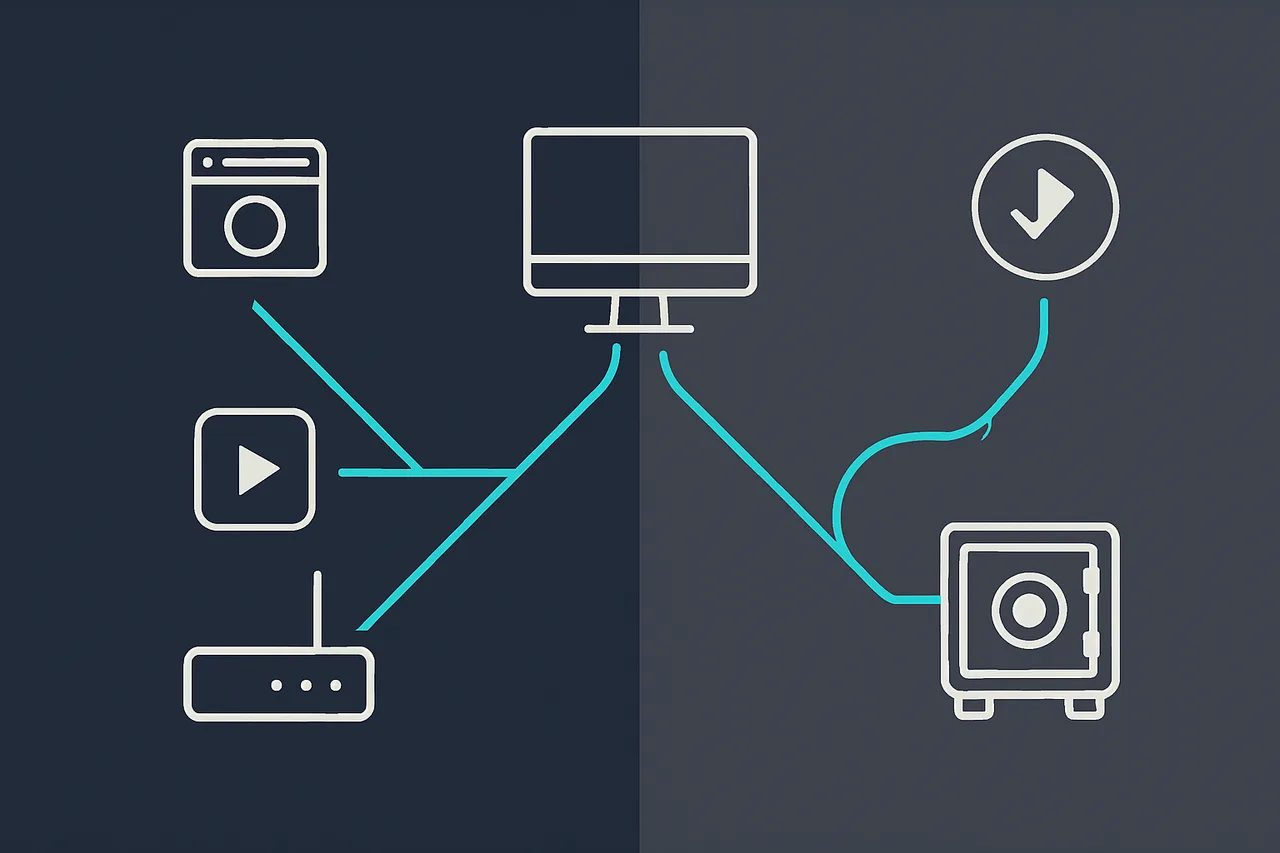
The challenge is that most VPN providers' built-in split tunneling features are either unreliable or don't offer the granular control needed for secure torrenting. Many users think they're protected when they're actually leaking their real IP address through DNS requests, IPv6 connections, or WebRTC vulnerabilities. A single misconfiguration can expose months or years of torrenting activity retroactively.
This guide will teach you multiple methods to achieve true split tunneling, from application-level binding to SOCKS5 proxy configurations. You'll learn how to verify your setup is working correctly, what to do if something goes wrong, and how to maintain your anonymity over time. By the end, you'll have a bulletproof torrenting setup that protects your privacy without sacrificing performance for other activities.
What You'll Need: Prerequisites and Requirements
Before diving into configuration, ensure you have the necessary components for a secure split tunneling setup. You'll need a VPN service that supports either SOCKS5 proxy connections or allows binding to specific network interfaces. I recommend services like Private Internet Access, NordVPN, or ExpressVPN, which offer both features and have proven track records for torrenting. Expect to pay between $3-12 monthly depending on your chosen service and subscription length.
For the torrent client, qBittorrent is the gold standard due to its robust proxy support, interface binding capabilities, and active development community. Download version 4.5.0 or newer from the official website, as earlier versions have known security vulnerabilities. Avoid uTorrent entirely – it's been compromised by adware and has poor privacy controls. The setup process typically takes 30-45 minutes for beginners, though experienced users can complete it in 10-15 minutes.
Your operating system choice affects the complexity of setup. Windows 10/11 offers the most straightforward configuration through built-in VPN clients and clear network interface identification. macOS requires slightly more technical knowledge due to its Unix-based networking stack, while Linux distributions offer the most control but demand familiarity with command-line tools and network configuration files.
Technical skill requirements are moderate – you should be comfortable navigating system settings, editing configuration files, and using command-line tools for testing. No programming knowledge is required, but basic networking concepts like IP addresses, ports, and proxies will be helpful. Have your VPN account credentials ready, including any SOCKS5 proxy settings provided by your service.
Understanding the Fundamentals: How Split Tunneling Actually Works
Split tunneling operates by creating selective routing rules that direct specific applications or traffic types through different network paths. At the network level, your computer maintains multiple routing tables – one for your regular internet connection and another for VPN traffic. When properly configured, your torrent client exclusively uses the VPN route while other applications default to your standard ISP connection.
There are three primary methods to achieve this separation. Application binding forces your torrent client to use only a specific network interface, such as your VPN's virtual adapter. If the VPN disconnects, the application loses all network access rather than falling back to your unprotected connection. SOCKS5 proxy routing creates an encrypted tunnel specifically for your torrent client without affecting system-wide traffic. Finally, advanced firewall rules can block torrent traffic on non-VPN interfaces while allowing other applications to function normally.
The security implications of each method vary significantly. Application binding provides the strongest protection because it creates a hard dependency on the VPN connection – no VPN means no torrent traffic, period. SOCKS5 proxies offer good protection but can fail silently if misconfigured, potentially exposing your real IP address. Firewall-based solutions require ongoing maintenance and can be bypassed by sophisticated applications or system updates.
Understanding these fundamentals helps you choose the right approach for your situation and recognize when something isn't working correctly. Many users think they're protected because their VPN client shows a connected status, but their torrent traffic is actually bypassing the tunnel due to misconfigured routing rules or application settings.
The key insight is that true split tunneling requires deliberate configuration at multiple levels – the VPN client, torrent application, and sometimes the operating system itself. Default settings are rarely sufficient for security-critical applications like torrenting, where a single IP leak can compromise months of careful privacy practices.
Complete qBittorrent Configuration Walkthrough
Begin by launching qBittorrent and navigating to Tools → Options → Advanced to enable the advanced interface if it's not already active. This unlocks critical security settings that aren't visible in the basic mode. The advanced interface provides granular control over network bindings, encryption settings, and proxy configurations that are essential for secure torrenting.
Navigate to Tools → Options → Connection to configure your network interface binding. In the "Network Interface" dropdown, select your VPN's virtual adapter rather than leaving it set to "Any interface." On Windows, this typically appears as "TAP-Windows Adapter" or similar, while macOS shows "utun0" or "utun1." Linux users will see "tun0" or the specific interface name assigned by their VPN client. This setting ensures qBittorrent can only connect through your VPN – if the VPN disconnects, torrenting stops completely.
⚠️ Warning: Never leave the network interface set to "Any interface" as this allows qBittorrent to fall back to your unprotected connection if the VPN fails. Always select the specific VPN adapter to ensure complete traffic isolation.
Configure the BitTorrent protocol settings by navigating to Tools → Options → BitTorrent. Enable "Anonymous mode" which disables features that could leak identifying information about your client or system. Set the encryption mode to "Require encryption" rather than "Prefer encryption" – this forces all peer connections to use encrypted communication and drops any unencrypted attempts. While this may slightly reduce the number of available peers, the security benefit is substantial.
In the Privacy section, disable all telemetry and automatic update checks. Turn off "Enable DHT to find more peers," "Enable Peer Exchange (PeX) to find more peers," and "Enable Local Peer Discovery to find more peers." These features can leak your real IP address even when using a VPN because they operate outside the normal BitTorrent protocol channels. Also disable "Send usage stats" and any crash reporting features that could transmit identifying information.
💡 Pro Tip: Create a test torrent download of a Linux distribution like Ubuntu to verify your configuration is working before downloading any copyrighted content. This allows you to test IP leak protection without legal risk.
Set up proper port configuration by navigating to Tools → Options → Connection and enabling "Use UPnP / NAT-PMP port forwarding from my router." However, more importantly, configure manual port forwarding through your VPN provider if they support it. Services like Private Internet Access provide specific ports for forwarding – configure qBittorrent to use these ports exclusively. This dramatically improves your seeding capability and overall torrent performance while maintaining security.
VPN Kill Switch Configuration and Network Interface Binding
A kill switch is your last line of defense against IP leaks, automatically cutting internet access if your VPN connection drops. Most VPN clients include built-in kill switches, but they're often ineffective for torrenting because they operate at the application level rather than blocking network traffic system-wide. Configure your VPN client's kill switch by accessing its settings menu and enabling "Network Lock," "Kill Switch," or similar terminology depending on your provider.
For Windows users, enhance the built-in kill switch by creating custom firewall rules through Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security. Navigate to Start → Windows Administrative Tools → Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security. Create an outbound rule that blocks qBittorrent.exe from accessing any network interface except your VPN adapter. This creates a secondary kill switch that operates independently of your VPN client software.
macOS users should configure the built-in pfctl firewall for additional protection. Create a custom firewall rule that blocks all traffic from qBittorrent except through the VPN interface. This requires editing the /etc/pf.conf file with administrator privileges and adding rules that specifically allow traffic only through your VPN's tunnel interface. The exact syntax varies depending on your VPN provider's interface naming convention.
⚠️ Warning: Always test your kill switch by deliberately disconnecting your VPN while a torrent is active. If you can still see download/upload activity after the VPN disconnects, your kill switch isn't working properly and needs additional configuration.
Linux users have the most control over kill switch configuration through iptables rules. Create rules that allow qBittorrent traffic only through the VPN interface while blocking it on all other interfaces. A typical rule set includes blocking all traffic from qBittorrent's process ID except through the tun0 interface, plus DNS leak prevention rules that force all DNS requests through the VPN tunnel. These rules persist across reboots if properly saved to your distribution's firewall configuration.
Port Forwarding Setup for Optimal Seeding Performance
Port forwarding dramatically improves your torrenting performance by allowing other peers to initiate connections directly to your client. Without port forwarding, you can only connect to peers who have forwarding enabled, significantly limiting your available peer pool and reducing download speeds. More importantly for the torrenting community, proper port forwarding makes you a better seeder, helping maintain healthy torrent ecosystems.
Start by checking if your VPN provider supports port forwarding – not all services offer this feature due to abuse concerns. Private Internet Access, AirVPN, and Windscribe are among the few providers that support port forwarding for torrenting. Log into your VPN provider's control panel and request a forwarded port, typically in the range of 1024-65535. Note this port number as you'll need it for qBittorrent configuration.
Configure qBittorrent to use your forwarded port by navigating to Tools → Options → Connection and entering the port number provided by your VPN service in the "Port used for incoming connections" field. Disable "Use UPnP / NAT-PMP port forwarding from my router" since you're using manual VPN port forwarding instead. Enable "Use different port on each startup" only if your VPN provider assigns dynamic ports that change with each connection.
💡 Pro Tip: Use online port checking tools like canyouseeme.org to verify your port forwarding is working correctly. The test should show your VPN's IP address, not your real IP, and confirm the port is open and accepting connections.
Some VPN providers require additional steps for port forwarding activation. Private Internet Access users must enable port forwarding in their client software and may need to reconnect to specific servers that support the feature. AirVPN provides a web-based control panel where you can configure multiple forwarded ports and assign them to specific devices or applications. Always verify that port forwarding is working after any VPN server changes or client updates.
Comprehensive IP Leak Testing and Verification Methods
Testing for IP leaks is crucial because even small configuration errors can expose your real identity to copyright holders and ISPs. Begin with basic IP address verification by visiting whatismyipaddress.com while your VPN is connected and qBittorrent is running. The displayed IP address should match your VPN server's location, not your actual geographic location. However, this basic test doesn't catch more sophisticated leaks that occur specifically during torrenting.
Perform torrent-specific IP leak testing using specialized tracking torrents designed to capture and report the IP addresses of connecting peers. Download a test torrent from ipmagnet.services.cbcdn.com, which creates a unique tracking page showing all IP addresses that connect to download the torrent. Start the download in qBittorrent and check the tracking page – only your VPN's IP address should appear, never your real IP.
Test for DNS leaks using dnsleaktest.com while torrenting is active. DNS leaks occur when your system resolves domain names through your ISP's DNS servers instead of your VPN's servers, potentially revealing your browsing activity and geographic location. Run both the standard and extended tests while qBittorrent is actively downloading. All DNS servers listed should belong to your VPN provider or generic services like Cloudflare, never your local ISP.
⚠️ Warning: IPv6 leaks are particularly dangerous because many VPN providers don't properly route IPv6 traffic through their tunnels. Disable IPv6 entirely on your system if your VPN doesn't explicitly support it, as IPv6 connections can bypass your VPN protection completely.
Conduct WebRTC leak testing using browserleaks.com/webrtc while your torrent client is running. WebRTC can expose your real IP address through browser-based applications even when using a VPN. While this primarily affects web browsing rather than torrenting directly, it can compromise your overall anonymity if you're researching torrents or accessing tracker websites through the same system.
Perform deliberate disconnection testing by starting a torrent download, then manually disconnecting your VPN while monitoring qBittorrent's network activity. Properly configured split tunneling should immediately stop all torrent traffic when the VPN disconnects. If you see continued download/upload activity after VPN disconnection, your configuration has failed and needs immediate correction before any real torrenting activity.
SOCKS5 Proxy Configuration as a Backup Method
SOCKS5 proxy configuration provides an excellent backup method for VPN split tunneling, offering application-level routing without affecting system-wide traffic. Unlike HTTP proxies that only handle web traffic, SOCKS5 proxies can route any type of network traffic, making them ideal for BitTorrent protocols. Many VPN providers offer SOCKS5 proxy access as an additional service, typically using different server infrastructure than their main VPN network.
Configure SOCKS5 in qBittorrent by navigating to Tools → Options → Connection → Proxy Server. Select "SOCKS5" from the type dropdown and enter your VPN provider's SOCKS5 server address and port number. These credentials are usually different from your main VPN login – check your provider's documentation for specific SOCKS5 server details. Enable "Use proxy for peer connections" and "Use proxy for RSS feeds and search" to ensure all torrent-related traffic routes through the proxy.
Authentication setup requires your VPN provider's specific SOCKS5 username and password, which may differ from your main account credentials. Private Internet Access users can find these credentials in their client area under "PPTP/L2TP/SOCKS Username and Password." NordVPN provides SOCKS5 access through specific server addresses listed in their knowledge base. Always use the dedicated SOCKS5 credentials rather than your main account login for security reasons.
💡 Pro Tip: Configure both VPN interface binding and SOCKS5 proxy simultaneously for maximum redundancy. If one method fails, the other provides backup protection. Just ensure both methods route through the same VPN provider to avoid conflicting IP addresses.
Test your SOCKS5 configuration using the same IP leak testing methods described earlier. The reported IP address should match your SOCKS5 proxy server's location, which may differ from your main VPN server location. Some providers operate separate infrastructure for SOCKS5 services, so seeing a different geographic location is normal as long as it's not your real location. Monitor qBittorrent's connection log to verify all peer connections are successfully routing through the SOCKS5 proxy.
Legal Considerations and DMCA Response Procedures
Understanding the legal landscape surrounding torrenting is crucial for making informed decisions about your privacy setup. In the United States, the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) requires ISPs to forward copyright infringement notices to subscribers whose IP addresses are detected sharing copyrighted content. These notices don't constitute legal action themselves, but they create a paper trail that copyright holders can use for future litigation. Receiving multiple notices can result in ISP account termination under their "three strikes" policies.
European Union countries operate under different legal frameworks, with some nations like the Netherlands and Switzerland having more permissive attitudes toward personal torrenting, while others like Germany and France actively pursue copyright enforcement. The UK's Digital Economy Act allows ISPs to throttle or disconnect users caught pirating repeatedly. Understanding your local laws helps determine the appropriate level of privacy protection needed for your situation.
If you receive a DMCA notice despite using VPN protection, it indicates a serious configuration failure that exposed your real IP address. Immediately stop all torrenting activity and review your setup for leaks. Common causes include VPN disconnections without proper kill switches, DNS leaks revealing your ISP, or IPv6 traffic bypassing your VPN tunnel. Document the exact time and date mentioned in the notice to correlate with your VPN logs and identify the specific failure point.
⚠️ Warning: Never ignore DMCA notices or assume they're fake. While many are automated and non-threatening, some represent the beginning of serious legal action. Respond appropriately according to your jurisdiction's laws and consider consulting with a lawyer if you receive multiple notices.
Proper DMCA notice response varies by jurisdiction and ISP. In the US, you can file a counter-notice if you believe the claim is invalid, but this reveals your identity to the copyright holder and should only be done with legal counsel. More commonly, users simply acknowledge receipt and ensure their privacy setup prevents future notices. Some ISPs offer "copyright alert" programs that provide warnings before taking action, giving you time to improve your security configuration.
Advanced Troubleshooting and Common Failure Points
VPN connection drops are the most common cause of IP leaks during torrenting. These can occur due to network instability, server overload, or ISP interference with VPN traffic. Monitor your VPN client's logs for frequent disconnections and switch to different servers or protocols if problems persist. OpenVPN over TCP port 443 often provides the most stable connection since it mimics HTTPS traffic that ISPs rarely block. WireGuard protocol offers better performance but may be more easily detected and throttled by some ISPs.
DNS configuration issues frequently compromise torrenting anonymity even when the main VPN tunnel is working correctly. Windows users should manually configure DNS servers in their network adapter settings to use their VPN provider's DNS servers rather than relying on automatic assignment. Set primary and secondary DNS to your VPN provider's servers, typically listed in their setup documentation. Flush your DNS cache using "ipconfig /flushdns" in Command Prompt after making changes.
Application binding failures occur when qBittorrent can't properly identify or connect to your VPN's network interface. This often happens after VPN client updates that change interface names or after Windows updates that reset network configurations. Verify your VPN interface name in Network Connections (Windows), Network Preferences (macOS), or using "ip addr show" (Linux). Update qBittorrent's interface binding if the name has changed.
💡 Pro Tip: Create a simple batch script or shell script that automatically checks your external IP address and compares it to your VPN provider's IP range. Run this script periodically to catch IP leaks before they become a problem.
Proxy authentication failures with SOCKS5 configurations usually indicate incorrect credentials or server information. Double-check that you're using SOCKS5-specific credentials rather than your main VPN account login. Some providers require enabling SOCKS5 access in your account settings before the credentials work. Clear any saved proxy passwords in qBittorrent and re-enter them manually to ensure they're correct.
Performance issues like slow speeds or connection timeouts can indicate configuration problems even when basic connectivity works. Disable IPv6 if your VPN doesn't support it properly, as mixed IPv4/IPv6 traffic can cause routing confusion. Adjust qBittorrent's connection limits – too many simultaneous connections can overwhelm VPN servers, while too few connections limit performance. Start with 200 global connections and 50 connections per torrent, adjusting based on performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I use free VPN services for torrenting? Free VPN services are generally unsuitable for torrenting due to severe limitations and security concerns. Most free services explicitly prohibit P2P traffic and will terminate accounts for torrenting. Those that allow it typically have bandwidth caps, slow speeds, and questionable privacy policies. Many free VPNs log user activity and some have been caught selling user data to third parties. The small cost of a reputable paid VPN service is worthwhile for the security and reliability needed for safe torrenting.
Will split tunneling slow down my torrent downloads? Split tunneling typically improves overall system performance compared to routing all traffic through a VPN, but torrent speeds may be slower than unprotected downloading. VPN servers add encryption overhead and routing delays that reduce maximum throughput. However, choosing nearby VPN servers, using WireGuard protocol, and proper port forwarding can minimize speed impacts. Most users find the security benefits far outweigh modest speed reductions.
Is it safe to torrent on public WiFi with a VPN? Torrenting on public WiFi networks carries additional risks even with VPN protection. Public networks are often monitored, and network administrators may detect high-bandwidth P2P traffic patterns even when encrypted. Some public WiFi systems actively block VPN connections or P2P protocols. If you must torrent on public WiFi, use additional obfuscation features like VPN over Tor or stealth VPN protocols that disguise VPN traffic as regular web browsing.
How often should I test for IP leaks? Perform comprehensive IP leak testing weekly during active torrenting periods and immediately after any system changes, VPN client updates, or network configuration modifications. Quick IP checks should be done before starting each torrenting session. Set up automated monitoring tools that alert you to IP changes or VPN disconnections. Regular testing helps catch configuration drift or software updates that compromise your privacy setup.
Can my ISP detect that I'm using a VPN for torrenting? ISPs can detect VPN usage through traffic analysis, but properly configured VPNs prevent them from seeing your actual torrenting activity. They may notice encrypted traffic patterns consistent with VPN use, but cannot determine what you're downloading or uploading. Some ISPs throttle all VPN traffic regardless of content, while others only target detected P2P traffic. Using obfuscated VPN protocols can help disguise VPN usage from ISP detection systems.
What should I do if my VPN provider doesn't support port forwarding? You can still torrent safely without port forwarding, though performance may be reduced since you can only connect to peers with open ports. Focus on popular torrents with many seeders to ensure adequate connection opportunities. Consider switching to a VPN provider that supports port forwarding if performance is unsatisfactory. Alternatively, use private trackers which often have better peer connectivity even without port forwarding due to their high seeder-to-leecher ratios.
Is it legal to use VPNs for torrenting? VPN usage is legal in most countries, including for torrenting, but downloading copyrighted content remains illegal regardless of privacy measures used. VPNs provide privacy protection and help avoid ISP throttling, but don't change the legal status of copyright infringement. Some countries like China, Russia, and UAE restrict VPN usage entirely. Always research your local laws and focus on legal torrenting activities like downloading Linux distributions, open-source software, and content released under Creative Commons licenses.
How do I know if my kill switch is working properly? Test your kill switch by deliberately disconnecting your VPN while actively torrenting and monitoring for continued network activity. Properly functioning kill switches immediately stop all torrent traffic when the VPN disconnects. Use network monitoring tools like NetLimiter (Windows), Little Snitch (macOS), or iftop (Linux) to verify no data flows from qBittorrent after VPN disconnection. Test both planned disconnections and simulated failures like disabling your network adapter to ensure comprehensive protection.
🏴☠️ Safe Torrenting with NordVPN
P2P-optimized servers in privacy-friendly countries (Panama, Switzerland). No throttling, strict no-logs policy, automatic kill switch prevents IP leaks mid-download. Split tunneling lets you route only torrent traffic through VPN.
[GET_P2P_PROTECTION]30-day money-back guarantee • No questions asked
Conclusion and Next Steps
Implementing proper split tunneling for torrent traffic requires careful attention to multiple configuration layers, from VPN client settings to application-specific bindings and system-level firewall rules. The methods outlined in this guide provide comprehensive protection against IP leaks while maintaining optimal performance for non-torrenting activities. Remember that security is an ongoing process – regular testing, monitoring, and updates are essential to maintain protection over time.
Your next steps should include implementing the configuration method that best suits your technical skill level and operating system, followed by thorough testing using the verification methods described. Start with basic IP leak tests and progress to more sophisticated monitoring as you become comfortable with the setup. Document your configuration choices and test results for future reference and troubleshooting.
Consider expanding your privacy setup beyond just torrenting by implementing DNS filtering, browser hardening, and additional network security measures. The skills you've learned in configuring split tunneling apply to many other privacy-focused networking scenarios. Stay informed about changes in copyright enforcement, VPN provider policies, and new privacy tools that can enhance your overall security posture.
Finally, remember that the best technical protection is worthless if not combined with smart torrenting practices. Focus on legal content when possible, use reputable trackers, maintain good seeding ratios, and stay informed about the legal landscape in your jurisdiction. A well-configured technical setup combined with thoughtful usage practices provides the strongest foundation for safe and private torrenting.